Technical Analysis
Key Components of Technical Analysis
Decoding Stock Trading Patterns
Stock trading is a world of patterns, and recognizing these recurring formations can be the key to understanding market behavior and making well-informed trading decisions. In this blog, we'll delve into the fascinating realm of stock trading patterns, exploring what they are, how they work, and how to use them to enhance your trading strategies.

Understanding Stock Trading Patterns
Stock trading patterns are visual representations of historical price movements that have a tendency to repeat over time. They reflect the psychological dynamics of the market, as traders and investors react to similar situations by buying, selling, or holding their positions. Recognizing these patterns can give you a valuable edge in your trading journey.

Cracking the Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern: A Guide to Spot, Trade, and Manage
In the world of stock trading, the Inverse Head and Shoulders pattern is a potent bullish reversal pattern that can be your ally in identifying trend reversals and making well-informed trading decisions. In this guide, we'll delve into the Inverse Head and Shoulders pattern, from its anatomy to trading strategies and risk management.

Understanding the Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern
The Inverse Head and Shoulders pattern is a bullish reversal pattern commonly spotted at the end of a downtrend. It comprises three troughs:
Left Shoulder: The first trough is typically part of the preceding downtrend.
Head: The central trough, the lowest of the three, indicates a brief plunge in price. It marks the climax of the previous downtrend.
Right Shoulder: The final trough, similar in depth to the left shoulder, appears after the head and typically signals a bullish trend reversal. Above these troughs, you'll find a "neckline" that connects the highest points of the price peaks between the troughs.
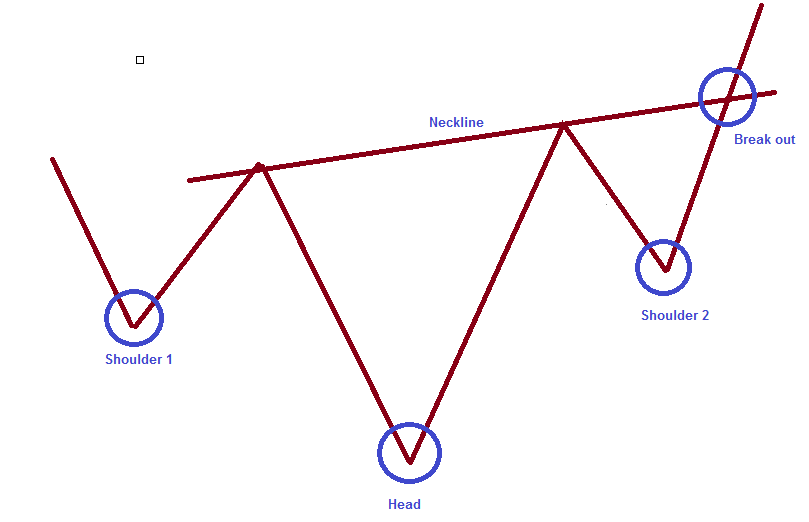
Recognizing the Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern
Identifying the Inverse Head and Shoulders pattern involves several key elements:
Shape: Look for the distinctive shape of three troughs and the neckline connecting the highs.
Volume: Volume should ideally decrease from the left shoulder to the head and increase from the head to the right shoulder. This suggests a lack of selling interest as the pattern develops and a surge in buying during the right shoulder.
Break of the Neckline: The pattern is typically confirmed when the price breaks above the neckline.

When to Enter and Exit with the Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern

Entering a Long Trade:
Entry Point: The ideal entry point is after the price breaks above the neckline. This break signifies confirmation of the pattern.
Stop-Loss: Place a stop-loss order below the right shoulder to protect against false breakouts.

Exiting the Trade:
Target: The target price is typically estimated by measuring the height from the head to the neckline and adding it to the neckline's breakout point.
Trailing Stop: As the price moves in your favor, consider using a trailing stop to lock in profits and protect your position.
Considerations and Risk Management
When trading the Inverse Head and Shoulders pattern, it's essential to keep several considerations in mind:
False Breakouts: Not all Inverse Head and Shoulders patterns lead to successful reversals. Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses in case of a false breakout.
Volume Confirmation: Pay attention to the volume profile. A significant increase in buying volume when the right shoulder is forming can strengthen the pattern's validity.
Time Frame: Patterns can vary in terms of timeframes. Consider the context of the pattern within the larger timeframe in which you're trading.
Confirmation: Wait for a clear and decisive breakout above the neckline before entering a trade.
Risk-Reward Ratio: Ensure that your potential reward justifies the risk you're taking on the trade. Calculate the risk-reward ratio to make informed decisions.
Mastering the Bullish Cup and Handle Pattern: A Guide to Identify, Trade, and Manage
The Bullish Cup and Handle Pattern is a remarkable bullish continuation pattern in stock trading that offers traders an opportunity to spot potential uptrend continuations and make well-informed trading decisions. In this guide, we'll explore the Bullish Cup and Handle Pattern in detail, from its structure to trading strategies and risk management.

Understanding the Bullish Cup and Handle Pattern
The Bullish Cup and Handle Pattern is a bullish continuation pattern that signifies a temporary consolidation phase within a prevailing uptrend. It consists of two key parts:
Cup: The Cup forms the first half of the pattern and resembles a cup or a rounded bottom. It signifies the initial bullish trend.
Handle: The Handle forms the latter half, usually taking the shape of a small downward-sloping consolidation. It indicates a brief pause in the uptrend before a potential continuation.

Recognizing the Bullish Cup and Handle Pattern
Identifying the Bullish Cup and Handle Pattern involves several key elements:
Cup Shape: The cup shape should be U-shaped, with a gradual upward curve.
Handle: The handle should be a small consolidation period, often sloping downward but remaining within a defined range.
Volume: Volume tends to decrease during the handle formation, indicating decreased interest or uncertainty among traders.

When to Enter and Exit with the Bullish Flag Pattern

Entering a Long Trade:
Entry Point: The ideal entry point is just above the upper trendline of the handle as the price breaks out.
Stop-Loss: Place a stop-loss order just below the lower trendline of the handle to protect against false breakouts.

Exiting the Trade:
Target: The target price can be estimated by measuring the depth of the cup and adding it to the breakout point.
Trailing Stop: As the price moves in your favor, consider using a trailing stop to lock in profits and protect your position.
Considerations and Risk Management
When trading the Bullish Cup and Handle Pattern, it's essential to keep several considerations in mind:
False Breakouts: Not all Bullish Cup and Handle Patterns lead to successful uptrend continuations. Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses in case of a false breakout.
Volume Confirmation: While handle formation typically involves decreasing volume, a breakout with a significant increase in volume can strengthen the pattern's validity.
Time Frame: Patterns can vary in terms of timeframes. Consider the context of the pattern within the larger timeframe in which you're trading.
Confirmation: Wait for a clear and decisive breakout above the upper trendline of the handle before entering a trade.

Unfurling the Bullish Flag Pattern: A Guide to Identify, Trade, and Manage
In the world of stock trading, the Bullish Flag Pattern is a powerful continuation pattern that can be your compass for identifying short-term trends within the larger market landscape. In this guide, we'll explore the Bullish Flag Pattern in detail, from its structure to trading strategies and risk management.
Read More
Understanding the Bullish Flag Pattern
The Bullish Flag Pattern is a bullish continuation pattern, typically seen after a sharp price increase (the "flagpole"). It's characterized by a rectangular consolidation phase (the "flag") that slopes against the prevailing trend. The pattern usually suggests a brief pause in the uptrend before it resumes.
Read More
Recognizing the Bullish Flag Pattern
Identifying the Bullish Flag Pattern involves several key elements:
Flagpole: The flagpole is the initial sharp price surge, indicating a strong bullish trend.
Flag: The flag is a rectangular-shaped consolidation period, characterized by price oscillation within a defined range. It slopes counter to the direction of the flagpole.
Volume: During the flag formation, volume often decreases, indicating reduced interest or uncertainty among traders.

When to Enter and Exit with the Bullish Flag Pattern

Entering a Long Trade:
Entry Point: The ideal entry point is just above the upper trendline of the flag as the price breaks out.
Stop-Loss: Place a stop-loss order just below the lower trendline of the flag to protect against false breakouts.

Exiting the Trade:
Target: The target price can be estimated by measuring the height of the flagpole and adding it to the breakout point.
Trailing Stop: As the price moves in your favor, consider using a trailing stop to lock in profits and protect your position.
Considerations and Risk Management
When trading the Bullish Flag Pattern, it's essential to keep several considerations in mind:
False Breakouts: Not all Bullish Flag Patterns lead to successful continuations. Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses in case of a false breakout.
Volume Confirmation: While flag formation typically involves decreasing volume, a breakout with a significant increase in volume can strengthen the pattern's validity.
Time Frame: Patterns can vary in terms of timeframes. Consider the context of the pattern within the larger timeframe in which you're trading.
Confirmation: Wait for a clear and decisive breakout above the upper trendline before entering a trade.
Risk-Reward Ratio: Ensure that your potential reward justifies the risk you're taking on the trade. Calculate the risk-reward ratio to make informed decisions.

Mastering the Double Bottom Pattern: A Guide to Recognize, Trade, and Manage
In the world of stock trading, the Double Bottom pattern is a versatile chart pattern that can help traders identify potential bullish trend reversals and make well-informed trading decisions. In this guide, we'll delve into the Double Bottom pattern in detail, from its structure to trading strategies and risk management.

Understanding the Double Bottom Pattern
The Double Bottom pattern is a bullish reversal pattern. It occurs after a strong downtrend and consists of two troughs that reach approximately the same price level, separated by a peak in between. This pattern suggests a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.

Recognizing the Double Bottom Pattern
Identifying the Double Bottom pattern involves several key elements:
Two Troughs: Identify two price troughs that are approximately at the same level, with a peak in between.
Volume: Volume typically decreases from the first trough to the peak and then increases as the pattern finalizes, suggesting reduced selling pressure.

When to Enter and Exit with the Double Bottom Pattern

Entering a Long Trade:
Entry Point: The ideal entry point is after the price breaks above the peak's resistance level, confirming the pattern.
Stop-Loss: Place a stop-loss order just below the second trough to protect against false breakouts.

Exiting the Trade:
Target: The target price can be estimated by measuring the distance between the peak and the trough and adding it to the breakout point.
Trailing Stop: As the price moves in your favor, consider using a trailing stop to lock in profits and protect your position.
Considerations and Risk Management
When trading the Double Bottom pattern, it's essential to keep several considerations in mind:
False Breakouts: Not all Double Bottom patterns lead to successful reversals. Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses in case of a false breakout.
Volume Confirmation: Look for volume patterns that align with the price movements. A surge in volume can confirm the validity of the pattern.
Time Frame: Patterns can vary in terms of timeframes. Consider the context within the larger timeframe in which you're trading.
Confirmation: Wait for a clear and decisive breakout before entering a trade.
Risk-Reward Ratio: Ensure that your potential reward justifies the risk you're taking on the trade. Calculate the risk-reward ratio to make informed decisions.
